Acne is a common skin condition that affects individuals of all ages, causing physical and emotional distress. While numerous treatments are available in the market, microdermabrasion has gained popularity as a potential solution for acne-prone skin. In this article, we will delve into the effectiveness of microdermabrasion in treating acne, exploring its benefits, considerations, and potential drawbacks.
Understanding Microdermabrasion:
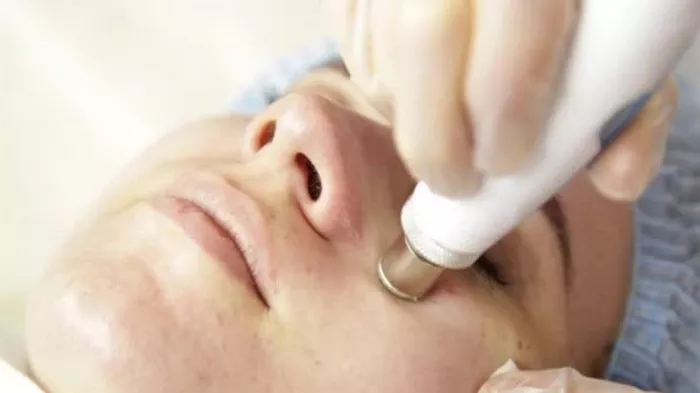
Microdermabrasion is a non-invasive cosmetic procedure that involves gently exfoliating the surface layer of the skin to remove dead skin cells and improve skin texture. This technique utilizes a handheld device equipped with tiny crystals or a diamond-tipped wand to achieve the desired exfoliation. The mechanical exfoliation stimulates cellular turnover, promoting collagen production and revealing fresher, rejuvenated skin.
The Mechanism of Action:
Microdermabrasion targets multiple factors contributing to acne development. Firstly, by removing the outermost layer of dead skin cells, microdermabrasion helps unclog pores, preventing the buildup of sebum, bacteria, and debris – major contributors to acne formation. Secondly, the exfoliation process promotes the shedding of skin cells, reducing the chances of pore blockage. Additionally, microdermabrasion encourages increased blood circulation, which aids in delivering oxygen and nutrients to the skin, supporting overall skin health.
Benefits of Microdermabrasion for Acne:
Exfoliation and Pore Cleansing: Microdermabrasion effectively clears away impurities and unclogs pores, reducing the occurrence of acne breakouts.
Reduced Hyperpigmentation: Acne often leaves behind dark spots and hyperpigmentation. By removing the damaged upper layers of the skin, microdermabrasion can help fade these marks over time, improving the appearance of post-acne pigmentation.
Enhanced Absorption of Topical Treatments: Microdermabrasion creates a clean and receptive canvas by removing the superficial layer of dead skin cells. This improves the penetration and efficacy of topical anti-acne medications, such as retinoids or benzoyl peroxide.
Improved Skin Texture: The exfoliation process in microdermabrasion promotes the growth of new skin cells, resulting in smoother, refined skin texture.
Considerations and Limitations:
Severity of Acne: Microdermabrasion is most effective for mild to moderate acne cases. Severe acne conditions may require additional or alternative treatments
Multiple Sessions: Significant improvements in acne usually require multiple sessions of microdermabrasion, typically spaced several weeks apart.
Downtime and Side Effects: While microdermabrasion is generally well-tolerated, it may cause temporary redness, sensitivity, or mild flaking. These side effects typically subside within a few days.
Suitability for All Skin Types: Microdermabrasion is generally safe for all skin types, but individuals with certain conditions like rosacea, active infections, or sunburned skin should avoid the procedure.
Conclusion:
Microdermabrasion can be a valuable addition to an acne treatment regimen, offering multiple benefits in managing acne-prone skin. By exfoliating the skin, unclogging pores, and improving overall skin health, microdermabrasion contributes to a clearer complexion and reduced acne breakouts. However, it is essential to consider individual skin conditions, consult with a skincare professional, and adopt a comprehensive approach tailored to one’s specific needs. With regular sessions and proper aftercare, microdermabrasion has the potential to enhance the appearance and quality of acne-affected skin.