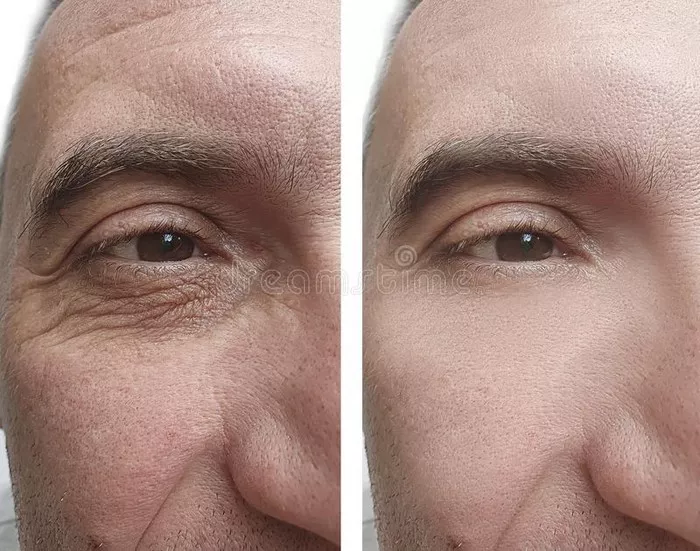
Wrinkles are a natural part of the aging process, but they can also be influenced by various external factors. As we age, our skin undergoes structural changes that lead to the formation of wrinkles. However, it is important to note that wrinkles can also develop prematurely due to lifestyle choices and environmental factors. In this article, we will explore the multiple causes of wrinkles, including intrinsic and extrinsic factors, and discuss preventive measures and treatment options.
I. Intrinsic Factors
Intrinsic factors refer to the natural aging process and genetic predispositions that contribute to the development of wrinkles.
Aging: As we age, our skin produces less collagen and elastin, proteins responsible for maintaining its elasticity and firmness. The gradual decline in these proteins leads to the thinning and sagging of the skin, resulting in the formation of wrinkles.
Genetics: Genetic factors play a significant role in determining how our skin ages. Some individuals may have a genetic predisposition to produce less collagen or have weaker elastin fibers, making them more prone to developing wrinkles at an earlier age.
Hormonal Changes: Hormonal fluctuations, particularly during menopause, can accelerate the aging process and contribute to the formation of wrinkles. Decreased estrogen levels reduce collagen production, leading to thinner and less elastic skin.
II. Extrinsic Factors
Extrinsic factors encompass external influences that contribute to the development of wrinkles, often causing premature aging.
Sun Exposure: Prolonged exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun is one of the primary causes of premature skin aging. UV rays damage collagen and elastin fibers, leading to the breakdown of these essential proteins and the formation of wrinkles. This process is known as photoaging.
Smoking: Smoking accelerates the aging process and increases the risk of developing wrinkles. The chemicals in tobacco smoke constrict blood vessels, reducing blood flow to the skin and depriving it of oxygen and nutrients. Additionally, smoking generates free radicals that damage collagen and elastin fibers.
Environmental Factors: Environmental pollutants, such as air pollution and toxins, can contribute to the development of wrinkles. These pollutants generate free radicals that cause oxidative stress, leading to collagen degradation and accelerated skin aging.
Repetitive Facial Expressions: Repeated facial movements, such as squinting, frowning, or smiling, can lead to the formation of dynamic wrinkles. Over time, these repetitive motions create creases in the skin that become more pronounced and permanent.
Poor Skincare Habits: Inadequate skincare routines, including failure to moisturize, cleanse, and protect the skin, can contribute to the development of wrinkles. Neglecting to use sunscreen or using harsh skincare products can also accelerate the aging process.
III. Preventive Measures
While it is impossible to completely prevent wrinkles, certain measures can help minimize their appearance and delay their onset.
Sun Protection: Applying broad-spectrum sunscreen with a high SPF, wearing protective clothing, and seeking shade during peak sun hours are crucial for preventing sun-induced wrinkles.
Healthy Lifestyle Choices: Adopting a healthy lifestyle can promote overall skin health. This includes maintaining a balanced diet rich in antioxidants, staying hydrated, getting regular exercise, and avoiding excessive alcohol consumption and smoking.
Skincare Routine: Establishing a consistent skincare routine is essential for maintaining youthful-looking skin. This should include gentle cleansing, moisturizing, and the use of products containing retinoids, antioxidants, and hyaluronic acid.
Facial Exercises: Engaging in facial exercises may help strengthen facial muscles and improve blood circulation, potentially reducing the appearance of wrinkles. However, further research is needed to determine their effectiveness.
IV. Treatment Options
Various treatment options are available for reducing the appearance of wrinkles and restoring a more youthful complexion.
Topical Treatments: Over-the-counter creams and serums containing retinoids, peptides, antioxidants, and hyaluronic acid can help improve the appearance of fine lines and wrinkles.
Medical Procedures: Dermatologists offer several medical procedures to address wrinkles, including chemical peels, microdermabrasion, laser resurfacing, dermal fillers, and botulinum toxin injections (e.g., Botox). These treatments target specific types of wrinkles and provide varying degrees of improvement.
Cosmetic Surgery: In severe cases, cosmetic surgery procedures like facelifts or brow lifts may be considered to tighten sagging skin and reduce the appearance of deep wrinkles.
Conclusion
Understanding the causes of wrinkles is crucial for implementing preventive measures and choosing appropriate treatment options. While intrinsic factors like aging and genetics are inevitable, extrinsic factors such as sun exposure, smoking, and poor skincare habits can be modified to minimize the development of wrinkles. By adopting a healthy lifestyle, practicing good skincare habits, and seeking professional guidance when necessary, individuals can maintain healthier, more youthful-looking skin for longer periods.