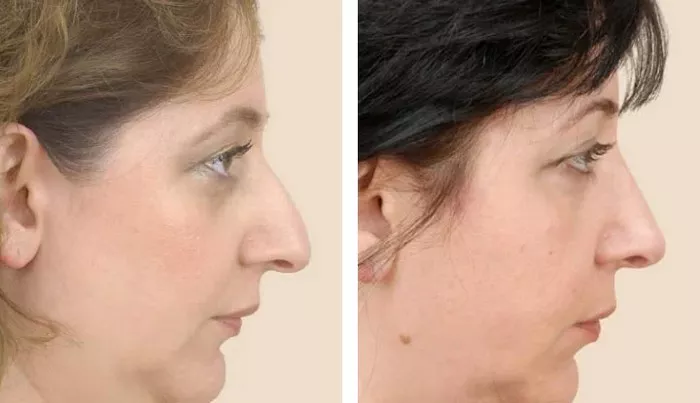
Rhinoplasty, also known as a nose job, is a surgical procedure that aims to reshape or reconstruct the nose. It is one of the most commonly performed cosmetic procedures, with a high success rate and low complication rate. Rhinoplasty can be performed on various parts of the nose, depending on the patient’s goals and the surgeon’s recommendations. This article will explore where on the body rhinoplasty is performed, the different types of rhinoplasty, and the outcomes and risks associated with the procedure.
The Anatomy of the Nose
Before discussing where on the body rhinoplasty is performed, it is important to understand the anatomy of the nose. The nose is composed of bone, cartilage, and soft tissue, and is divided into two nasal passages by the septum. The nasal passages are lined with mucous membranes that help to warm, humidify, and filter the air we breathe. The nose also plays an important role in our sense of smell.
Rhinoplasty can be performed on various parts of the nose, including the bridge, tip, nostrils, and septum. The specific areas targeted during rhinoplasty will depend on the patient’s goals and the surgeon’s recommendations.
Types of Rhinoplasty
There are two main types of rhinoplasty: open and closed. Open rhinoplasty involves making an incision on the columella, the strip of tissue that separates the nostrils, and lifting the skin and soft tissue to access the underlying structures of the nose. Closed rhinoplasty, on the other hand, involves making incisions inside the nostrils and accessing the underlying structures through these incisions.
Open rhinoplasty allows for greater visibility and control during the procedure, making it a preferred technique for more complex cases. Closed rhinoplasty, however, typically results in less scarring and a shorter recovery time.
Rhinoplasty can also be classified as functional or cosmetic. Functional rhinoplasty aims to improve nasal breathing and related symptoms, such as chronic congestion or snoring. Cosmetic rhinoplasty, on the other hand, aims to improve the appearance of the nose, such as reducing the size of a prominent hump or refining the tip.
Where on the Body is Rhinoplasty Performed?
Rhinoplasty can be performed on various parts of the nose, depending on the patient’s goals and the surgeon’s recommendations. The most common areas targeted during rhinoplasty include the bridge, tip, nostrils, and septum.
Bridge Rhinoplasty
Bridge rhinoplasty involves reshaping the bridge of the nose, which is the bony and cartilaginous structure that runs from the forehead to the tip of the nose. This may involve reducing the size of a prominent hump, straightening a crooked bridge, or adding volume to a flat bridge.
Tip Rhinoplasty
Tip rhinoplasty involves reshaping the tip of the nose, which is the lowermost part of the nose that protrudes from the face. This may involve reducing the size of a bulbous or drooping tip, refining the shape of the tip, or rotating the tip upward or downward.
Nostril Rhinoplasty
Nostril rhinoplasty involves reshaping the nostrils, which are the openings at the base of the nose that allow air to enter and exit. This may involve reducing the size of flared nostrils, correcting asymmetrical nostrils, or improving the overall shape and symmetry of the nostrils.
Septoplasty
Septoplasty is a type of rhinoplasty that involves correcting a deviated septum, a condition where the thin wall that separates the nasal passages is displaced to one side, causing breathing difficulties, nasal congestion, and other related symptoms. Septoplasty may be performed alone or in combination with other types of rhinoplasty to improve the overall function and appearance of the nose.
Outcomes and Risks of Rhinoplasty
Rhinoplasty is generally considered a safe and effective procedure, with a high success rate and low complication rate. Studies have reported that up to 90% of patients are satisfied with the results of their rhinoplasty, with few complications, such as bleeding, infection, and scarring.
However, like any surgery, rhinoplasty does carry some risks and potential complications. The most common complications of rhinoplasty include bleeding, infection, and anesthesia-related complications, such as allergic reactions or respiratory problems. Other potential complications of rhinoplasty include scarring, asymmetry, and changes in the patient’s sense of smell or taste.
To minimize the risk of complications, it is important to choose a qualified and experienced surgeon and to follow all pre- and post-operative instructions carefully. Patients should also inform their surgeon of any medications they are taking, as some medications, such as blood thinners, may need to be temporarily discontinued before the procedure.
Recovery and Follow-up Care
Most patients can return to normal activities within a week after rhinoplasty, although full recovery may take several weeks. Patients may experience some swelling, bruising, and discomfort in the days following the procedure, which can be managed with pain medication and cold compresses.
To promote healing and reduce the risk of complications, patients should avoid blowing their nose or engaging in strenuous activity for several weeks after the procedure. Patients should also keep the nasal passages moist with saline sprays or drops and avoid smoking or exposure to secondhand smoke.
Patients should follow up with their surgeon as directed to monitor their progress and ensure proper healing. In some cases, additional procedures or therapies may be recommended to further improve nasal function and related symptoms.
Conclusion
Rhinoplasty is a safe and effective procedure that can improve the appearance and function of the nose. The specific areas targeted during rhinoplasty will depend on the patient’s goals and the surgeon’s recommendations. Rhinoplasty can be performed using open or closed techniques, and may be classified as functional or cosmetic. Although rhinoplasty does carry some risks and potential complications, these can be minimized with proper care and follow-up. Patients should choose a qualified and experienced surgeon and follow all pre- and post-operative instructions carefully to ensure the best possible outcome.