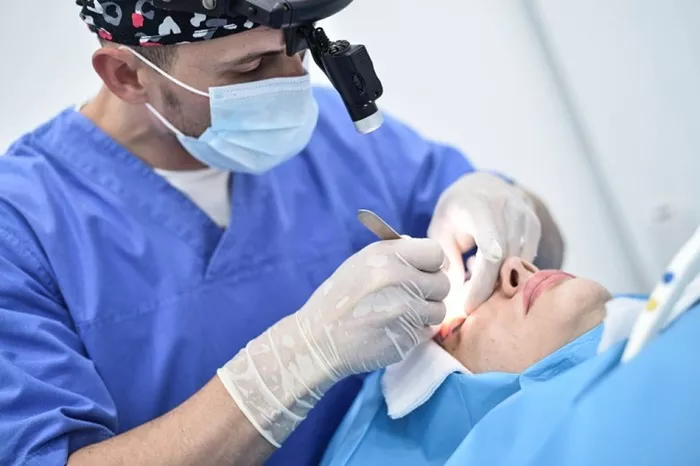
Upper eyelid surgery, also known as upper blepharoplasty, is a common cosmetic procedure designed to remove excess skin, fat, or muscle from the upper eyelids. It is often performed to rejuvenate the appearance of the eyes, making them look more open and youthful, while sometimes improving vision that has been impaired by sagging skin. In this article, we will explore the steps involved in upper eyelid surgery, the medical and aesthetic benefits, potential risks, and aftercare.
What Is Upper Eyelid Surgery?
Upper eyelid surgery is a procedure that targets the upper eyelid to remove extra skin, which can create a drooping or heavy-lidded appearance. Over time, as skin loses its elasticity, excess skin can gather on the eyelids, creating a tired, older appearance. In some cases, this sagging can impair peripheral vision. Upper blepharoplasty can correct these issues by tightening the skin and removing any unnecessary fat or muscle tissue.
The surgery can be performed for both medical and cosmetic reasons. Many individuals undergo this procedure to enhance their appearance, while others may do so to improve their vision or reduce discomfort caused by drooping skin.
Medical Indications for Upper Eyelid Surgery
In addition to cosmetic motivations, upper eyelid surgery may be recommended for medical reasons. These include:
Dermatochalasis: This is a condition where excess eyelid skin creates folds that hang down over the eyelashes, impairing vision.
Ptosis: In some cases, the muscles responsible for lifting the eyelids weaken, leading to drooping eyelids. Upper blepharoplasty can correct this by tightening the muscles.
Vision Impairment: Excess skin on the eyelids can interfere with peripheral vision, making everyday activities like reading or driving difficult.
Who Is a Candidate for Upper Eyelid Surgery?
Anyone who experiences sagging upper eyelids or puffiness caused by excess fat may be a candidate for upper blepharoplasty. Good candidates for surgery typically include:
- Individuals over the age of 30, as sagging eyelid skin becomes more common with age.
- Healthy individuals without severe eye conditions.
- People who do not smoke, as smoking can affect healing and increase the risk of complications.
Preoperative Consultation
Before undergoing upper eyelid surgery, patients should have a thorough consultation with a qualified plastic surgeon or oculoplastic surgeon. During this consultation, the surgeon will assess the patient’s medical history, current health, and specific concerns about their eyelids. The surgeon may also conduct a vision test to determine whether the surgery is necessary for medical reasons.
In addition, the surgeon will evaluate the patient’s eyelid anatomy to determine how much skin, fat, or muscle needs to be removed. They may also discuss the desired cosmetic outcomes with the patient and explain what to expect from the procedure, including any potential risks and complications.
See also: Is Upper Eyelid Surgery Safe? All You Need to Know!
How Upper Eyelid Surgery Is Performed
Step 1: Anesthesia
Upper eyelid surgery is usually performed under local anesthesia with sedation, but in some cases, general anesthesia may be used. Local anesthesia involves numbing the area around the eyelids so that the patient does not feel pain during the procedure. Sedation may be administered to help the patient relax and remain comfortable. With general anesthesia, the patient is completely unconscious throughout the surgery.
Step 2: Marking the Eyelid
Once the patient is anesthetized, the surgeon marks the eyelid with a surgical marker to outline where incisions will be made. The markings help guide the surgeon in removing the correct amount of skin, fat, or muscle tissue. Precise markings are crucial to ensure symmetry between both eyelids and to achieve the desired cosmetic or functional outcome.
Step 3: Making the Incisions
The surgeon begins the procedure by making a small incision along the natural crease of the upper eyelid. This placement allows the resulting scar to be concealed within the eyelid crease once the incision heals. The length of the incision will depend on the amount of excess skin or fat that needs to be removed.
In some cases, the surgeon may also make additional incisions to target specific areas of fat that are causing puffiness or bulging around the eyes. These incisions are typically small and carefully placed to minimize visible scarring.
Step 4: Removing Excess Skin, Fat, and Muscle
After making the incision, the surgeon carefully removes excess skin, fat, and muscle tissue from the eyelid. The amount of tissue removed depends on the patient’s individual needs and goals for the surgery. In most cases, only a small amount of tissue is removed to avoid causing the eyelid to appear too tight or unnatural.
If fat pockets are contributing to a puffy appearance, the surgeon will gently remove or reposition the fat to create a smoother contour around the eye. Muscle tissue may also be tightened or adjusted to improve the eyelid’s function and appearance.
Step 5: Closing the Incision
Once the necessary adjustments have been made, the surgeon closes the incision using small, delicate sutures. These stitches are typically placed within the natural crease of the eyelid, making the resulting scar less noticeable. In some cases, the surgeon may use absorbable sutures that dissolve on their own, while in other cases, non-absorbable sutures are used and must be removed after a few days.
To protect the area and promote healing, the surgeon may apply small adhesive strips or a light bandage to the eyelid.
Step 6: Postoperative Care and Recovery
Following surgery, patients are given specific instructions for postoperative care. This typically includes:
Using cold compresses to reduce swelling and bruising around the eyes.
Applying prescribed ointments or eye drops to prevent infection and keep the area moisturized.
Taking pain medication to manage any discomfort during the initial recovery period.
Avoiding strenuous activity for at least one week, including heavy lifting and vigorous exercise.
Keeping the head elevated during sleep to reduce swelling.
Most patients experience mild swelling and bruising for the first week following surgery, but these symptoms gradually subside. Full recovery typically takes 1 to 2 weeks, after which the patient can resume normal activities, including wearing makeup and contact lenses.
Step 7: Follow-Up Appointments
After the procedure, patients will have follow-up appointments with their surgeon to monitor the healing process. These appointments are important to ensure that the eyelids are healing properly and that there are no complications, such as infection or excessive scarring.
In cases where non-absorbable sutures were used, the surgeon will remove them during a follow-up visit, typically within 5 to 7 days after surgery.
Risks and Complications of Upper Eyelid Surgery
Like any surgical procedure, upper blepharoplasty carries some risks. While most patients experience a smooth recovery, it is important to be aware of potential complications, including:
Infection: Although rare, infections can occur following surgery. Patients are typically prescribed antibiotics to reduce this risk.
Excessive Bleeding: Minor bleeding is normal after surgery, but excessive or prolonged bleeding should be reported to the surgeon.
Scarring: While the incisions are carefully placed to minimize visible scarring, some patients may develop more noticeable scars depending on their skin type and healing process.
Asymmetry: In some cases, the eyelids may heal unevenly, leading to asymmetry between the eyes. Additional corrective surgery may be necessary in these cases.
Dry Eyes: Some patients experience dry eyes following upper eyelid surgery. This is typically temporary, but in rare cases, it can become a long-term issue.
Vision Problems: In rare instances, patients may experience temporary vision changes following surgery. Severe vision problems are very uncommon but should be immediately reported to the surgeon.
How to Minimize Risks
Patients can minimize the risk of complications by choosing a qualified and experienced surgeon, following all preoperative and postoperative instructions, and attending all scheduled follow-up appointments. It is also important for patients to disclose any pre-existing medical conditions, medications, or lifestyle habits, such as smoking, that may affect the outcome of the surgery.
Results and Long-Term Outlook
The results of upper eyelid surgery are generally long-lasting, with most patients enjoying a more youthful, alert appearance for many years. The longevity of the results depends on several factors, including the patient’s skin type, age, and overall health. While upper blepharoplasty can create a more youthful appearance, it does not stop the natural aging process, and some patients may eventually require a second procedure if additional sagging occurs.
The majority of patients are highly satisfied with the results of their upper eyelid surgery, especially when the procedure is performed by a skilled and experienced surgeon. Many patients report feeling more confident and looking more refreshed following the surgery.
Conclusion
Upper eyelid surgery is a highly effective procedure for rejuvenating the appearance of the eyes and improving vision in cases of sagging skin. The surgery is relatively quick, with minimal downtime, and provides long-lasting results for both medical and cosmetic concerns. By understanding the steps involved in upper blepharoplasty and carefully following postoperative instructions, patients can achieve a more youthful, alert, and refreshed appearance with minimal risk of complications.
Related topic:
How to Reduce Swelling on the Upper Eyelid?
How long does upper eyelid surgery take to heal?
How Can I Tighten My Upper Eyelids Without Surgery: [Revealed!]