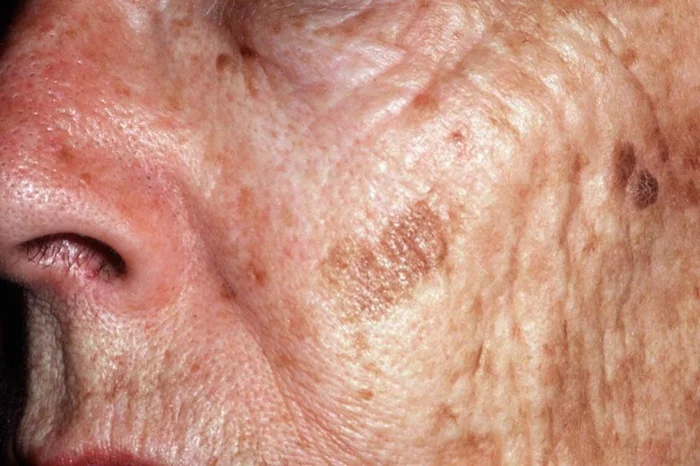
As people age, their bodies go through various changes. One of the most visible changes is the appearance of spots on the skin, often referred to as “age spots” or “liver spots.” These spots are common, especially in older adults. They are harmless in most cases, but their appearance can cause concern. In this article, we will explore why older people get spots, how they form, and what can be done to prevent or treat them. Understanding the underlying causes helps in managing their appearance and taking care of skin health as we age.
What Are Age Spots?
Age spots, also known as solar lentigines, are flat, brown, black, or gray spots that typically appear on the skin in areas frequently exposed to the sun, such as the face, hands, shoulders, and arms. They are usually seen in people over the age of 50, but younger people can also develop them, especially if they have excessive sun exposure.
Characteristics of Age Spots
Size: Age spots can vary in size from a small freckle to about half an inch across.
Color: They range in color from light brown to black, depending on a person’s skin tone and the level of melanin production.
Shape: They are usually round or oval and have clearly defined edges.
Texture: Age spots are flat, unlike moles or other raised skin lesions.
Why Do Age Spots Develop?
The primary cause of age spots is the overproduction of melanin, the pigment responsible for skin color. There are several contributing factors to why melanin production becomes uneven, leading to the formation of spots.
1. Sun Exposure
Ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun is the most significant factor in the development of age spots. When the skin is exposed to the sun, melanin is produced to help protect the deeper layers of the skin from UV damage. Over time, repeated sun exposure causes melanin to accumulate in certain areas, leading to the appearance of age spots. This is why age spots are more common on areas of the skin that have had the most exposure to the sun, such as the face, hands, arms, and shoulders.
The Role of UV Radiation
UV radiation from the sun comes in two forms: UVA and UVB. Both types can damage the skin, but UVA rays are more responsible for premature aging and the formation of age spots. They penetrate deeper into the skin, causing long-term damage to skin cells and promoting uneven melanin production.
2. Aging
As people age, the skin becomes less able to regenerate after sun exposure or other forms of damage. The turnover of skin cells slows down, and this can lead to the accumulation of pigment in certain areas, resulting in spots. Additionally, the skin’s natural ability to repair itself declines with age, making it more susceptible to damage from environmental factors like UV rays.
3. Genetic Factors
Some individuals are more genetically predisposed to developing age spots. People with lighter skin tend to develop age spots more frequently because they have less melanin in their skin to begin with. However, people with darker skin can also develop them, especially if they have had significant sun exposure.
4. Hormonal Changes
Hormonal changes, particularly in women, can also contribute to the formation of age spots. For example, during pregnancy or menopause, fluctuations in hormone levels can cause changes in melanin production, leading to hyperpigmentation and the development of dark spots.
5. Free Radical Damage
Free radicals are unstable molecules that can damage cells and contribute to aging. They are generated by environmental factors such as UV radiation, pollution, and cigarette smoke. Free radicals can damage skin cells, leading to inflammation and uneven pigmentation. Over time, this damage accumulates, contributing to the formation of age spots.
Types of Spots Older People Get
Aside from age spots, older adults may develop several other types of spots or discoloration on their skin. These can be caused by different factors, including underlying health conditions.
1. Seborrheic Keratosis
Seborrheic keratosis is a non-cancerous skin growth that often appears in older adults. It can look like a raised, wart-like spot or a flat, brown patch. These growths are usually harmless but can be mistaken for other types of skin lesions, such as moles or melanomas. They typically appear on the face, chest, shoulders, or back.
2. Lentigo
Lentigo is a type of dark spot that develops due to excessive sun exposure, much like age spots. There are two main types of lentigo: solar lentigo (caused by sun exposure) and lentigo simplex (unrelated to sun exposure). Both types can appear as small, dark patches on the skin, similar to freckles, but they tend to be larger and more defined.
3. Melasma
Melasma is a skin condition characterized by dark, irregularly shaped patches, usually on the face. It is more common in women and is often triggered by hormonal changes, such as pregnancy or menopause. Although melasma can affect people of any age, it becomes more prevalent with age and sun exposure.
4. Actinic Keratosis
Actinic keratosis is a rough, scaly patch that develops on the skin due to prolonged sun exposure. It is considered a precancerous lesion, as it can develop into skin cancer if left untreated. Actinic keratosis spots tend to be red, pink, or brown, and they often feel rough to the touch.
See also: How to Get Rid of Age Spots?
Prevention of Age Spots
Although age spots are a natural part of the aging process, there are several ways to prevent or minimize their appearance. The key to prevention lies in protecting the skin from damage and promoting overall skin health.
1. Sun Protection
The most effective way to prevent age spots is to protect the skin from the sun. This can be achieved through a combination of the following strategies:
Using Sunscreen: Applying a broad-spectrum sunscreen with at least SPF 30 every day can significantly reduce the risk of developing age spots. Sunscreen should be applied to all exposed areas of the skin, even on cloudy days.
Wearing Protective Clothing: Long-sleeved shirts, wide-brimmed hats, and sunglasses can help shield the skin from UV radiation. Choosing clothing made from tightly woven fabrics can offer additional protection.
Avoiding Peak Sun Hours: The sun’s rays are strongest between 10 a.m. and 4 p.m. Avoiding sun exposure during these hours can help reduce the risk of skin damage.
2. Regular Skin Care
Maintaining a good skincare routine can help keep the skin healthy and may reduce the appearance of age spots. This includes:
Cleansing: Washing the skin regularly with a gentle cleanser to remove dirt, oil, and other impurities.
Exfoliating: Regular exfoliation helps to remove dead skin cells and promote the growth of new, healthy skin cells.
Moisturizing: Keeping the skin moisturized can help maintain its elasticity and prevent it from becoming dry and damaged.
3. Antioxidants
Incorporating antioxidants into your skincare routine can help protect the skin from free radical damage. Antioxidants, such as vitamin C, vitamin E, and beta-carotene, neutralize free radicals and reduce inflammation, which can help prevent the development of age spots.
4. Healthy Diet
A balanced diet rich in vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants can support skin health and help prevent age spots. Foods that are high in antioxidants, such as fruits and vegetables, can help protect the skin from damage caused by free radicals.
5. Avoiding Tanning Beds
Tanning beds emit UVA rays, which can accelerate skin aging and increase the risk of developing age spots. Avoiding tanning beds can help protect the skin and reduce the likelihood of developing spots.
Treatment Options for Age Spots
If age spots have already developed, there are several treatment options available to reduce their appearance. These treatments range from topical creams to more advanced dermatological procedures.
1. Topical Treatments
There are various over-the-counter and prescription creams available that can help lighten age spots. These creams often contain ingredients such as:
Hydroquinone: A skin-lightening agent that reduces melanin production and helps fade dark spots.
Retinoids: Vitamin A derivatives that promote cell turnover and can help lighten age spots over time.
Alpha Hydroxy Acids (AHAs): Exfoliating agents that help remove dead skin cells and promote the growth of new, healthy skin cells.
2. Chemical Peels
Chemical peels involve applying a chemical solution to the skin, which causes the outer layer of the skin to peel away. This procedure can help remove age spots by encouraging the growth of new skin. There are different types of chemical peels, ranging from mild to deep, depending on the severity of the spots.
3. Laser Therapy
Laser therapy is a popular treatment for age spots. It involves using a laser to target the pigment in the spots and break it down. This procedure is typically done in a dermatologist’s office and may require multiple sessions for the best results.
4. Cryotherapy
Cryotherapy involves freezing the age spots with liquid nitrogen, causing them to peel off over time. This treatment is often used for individual spots and is a quick and effective way to remove them.
5. Microdermabrasion
Microdermabrasion is a non-invasive procedure that involves exfoliating the outer layer of the skin with tiny crystals. This treatment can help reduce the appearance of age spots by removing dead skin cells and promoting the growth of new skin.
When to See a Doctor
Although age spots are usually harmless, it is essential to monitor any changes in the skin and consult a dermatologist if:
- A spot changes in size, shape, or color.
- The spot has irregular borders or multiple colors.
- The spot bleeds, itches, or becomes tender.
These could be signs of skin cancer, and early detection is crucial for successful treatment.
Conclusion
Age spots are a common part of the aging process, primarily caused by sun exposure, genetic factors, and the natural aging of the skin. While they are generally harmless, they can be a cosmetic concern for many people. By taking preventive measures, such as protecting the skin from the sun, maintaining a healthy skincare routine, and eating a balanced diet, it is possible to reduce the risk of developing age spots. For those who already have age spots, various treatment options are available to lighten or remove them. It is essential to stay informed about skin health and consult a healthcare provider if there are any concerns about changes in the skin.
By understanding the causes and treatments for age spots, individuals can take better care of their skin as they age, ensuring it remains healthy and vibrant for as long as possible.
Related topic:
Do freckles turn into age spots?
How to reduce age spots on face naturally?
Does Roc Retinol Fade Dark Spots?