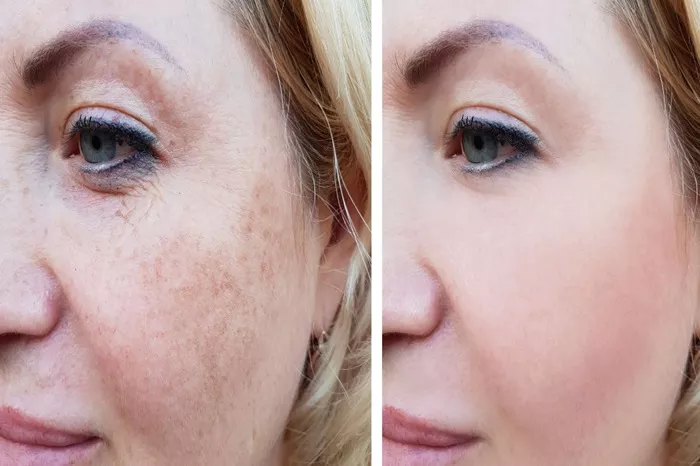
Skin pigmentation issues, such as dark spots, melasma, and freckles, are common skin concerns that many people seek to treat. These conditions arise due to an overproduction of melanin, the pigment responsible for the color of our skin, hair, and eyes. Over the years, various treatment methods have emerged to address pigmentation, with laser treatment standing out as one of the most effective and advanced solutions. But the question remains: Can a laser really remove skin pigmentation? This article delves into the science, types of laser treatments available, their effectiveness, safety, and potential side effects to answer this question.
Understanding Skin Pigmentation
What Is Skin Pigmentation?
Skin pigmentation refers to the coloring of the skin. Melanin is produced by cells called melanocytes, which are present in the epidermis, the outermost layer of the skin. The more melanin produced, the darker the skin tone becomes. However, when melanocytes produce too much or too little melanin, it leads to pigmentation disorders such as:
Hyperpigmentation: An excess of melanin production causes darker patches or spots on the skin.
Hypopigmentation: A reduction in melanin production leads to lighter patches of skin.
Common Types of Hyperpigmentation
There are several conditions where the skin becomes hyperpigmented:
Melasma: A condition often seen in pregnant women or those taking hormonal treatments, melasma presents as dark, irregular patches usually on the face.
Sunspots (Solar Lentigines): These are caused by prolonged sun exposure and commonly appear on areas frequently exposed to the sun, such as the face, hands, and shoulders.
Freckles: Small brown spots, often genetic, but can become darker with sun exposure.
Post-Inflammatory Hyperpigmentation (PIH): This results from skin injury or inflammation, such as acne, eczema, or psoriasis, which triggers excess melanin production in the healing process.
What Causes Skin Pigmentation?
Pigmentation is influenced by various factors, including:
Sun Exposure: UV rays from the sun trigger melanocytes to produce more melanin as a protective response. Repeated exposure can lead to hyperpigmentation over time.
Hormonal Changes: Fluctuations in hormones, especially during pregnancy or while taking birth control pills, can cause conditions like melasma.
Genetic Factors: Freckles and other forms of pigmentation can be inherited from family members.
Inflammation or Injury: Skin trauma, such as cuts, burns, or acne, can stimulate excessive melanin production as the skin heals.
Medications: Some medications, like certain antibiotics or chemotherapy drugs, can trigger hyperpigmentation as a side effect.
With this understanding of skin pigmentation and its causes, the question now arises: how does laser treatment work to address these concerns?
How Do Lasers Treat Pigmentation?
What Is Laser Treatment?
Laser treatments use focused light energy to target specific cells in the skin. This energy is absorbed by the pigment (melanin) in the skin, effectively breaking down the excess melanin in the pigmented areas. Over time, the body’s natural healing process removes these pigment particles, leaving the skin tone more even and balanced.
Mechanism of Laser Treatment for Pigmentation
Laser treatments for pigmentation work on a principle called selective photothermolysis. This means that the laser light selectively targets the pigment in the skin without affecting the surrounding healthy tissue. The light energy is absorbed by the dark melanin in the pigmented spots, which heats up and breaks apart the pigment into smaller fragments. These pigment particles are then naturally cleared away by the body’s immune system.
There are different types of lasers used for pigmentation treatment, each with its own unique properties and wavelengths that determine their effectiveness and suitability for specific pigmentation types.
Types of Laser Treatments for Pigmentation
1. Q-Switched Nd Laser
The Q-Switched Nd laser is one of the most commonly used lasers for pigmentation removal. It emits short, high-energy pulses of light that target the melanin in the skin. This laser is effective for treating:
- Freckles
- Sunspots
- Post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation (PIH)
The Q-Switched laser is often favored because it can treat both superficial and deeper pigmentation. It has a lower risk of causing post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation, making it suitable for people with darker skin tones.
2. Fractional Laser (Fraxel)
The Fraxel laser is a type of fractional laser that works by creating tiny, controlled micro-injuries in the skin. These micro-injuries stimulate the skin’s natural healing process, promoting collagen production and skin regeneration. While it’s primarily used for resurfacing the skin and treating fine lines and wrinkles, it is also effective for pigmentation issues like:
- Melasma
- Sun damage
Fraxel lasers are particularly useful for treating larger areas of pigmentation, such as those caused by sun exposure.
3. Pico Laser
The Pico laser is a newer technology that delivers ultra-short bursts of energy in picoseconds (trillionths of a second). This fast delivery allows the laser to break down pigment into even smaller particles, which are more easily absorbed by the body. The Pico laser is especially effective for treating stubborn pigmentation such as:
- Melasma
- Freckles
- Tattoo removal
The advantage of the Pico laser is that it minimizes damage to the surrounding tissue, leading to faster recovery times and fewer side effects.
4. IPL (Intense Pulsed Light)
While technically not a laser, IPL uses a broad spectrum of light to target pigmentation. It’s commonly used for treating:
- Sunspots
- Freckles
IPL is less aggressive than laser treatments and is often used for patients with mild to moderate pigmentation concerns. It’s also used for overall skin rejuvenation, as it can improve skin tone and texture.
See also: Can Pico Laser Remove Pigmentation?
Effectiveness of Laser Treatment for Pigmentation
How Effective Are Lasers for Pigmentation?
The effectiveness of laser treatments for pigmentation varies depending on several factors, including the type of pigmentation, skin type, and the laser technology used. Generally, lasers are highly effective at reducing or completely removing pigmentation, but the results can vary from person to person.
For example:
Superficial pigmentation, like sunspots and freckles, often respond well to laser treatments and can fade significantly after just one or two sessions.
Deeper pigmentation, like melasma, can be more challenging to treat. While lasers can improve the appearance of melasma, they are often used in combination with other treatments, such as topical creams or chemical peels, for optimal results.
How Many Sessions Are Required?
The number of sessions required depends on the severity and depth of the pigmentation. Superficial pigmentation may only need one to three sessions, while deeper pigmentation may require four to six sessions or more. The sessions are typically spaced a few weeks apart to allow the skin time to heal between treatments.
Long-Term Results
Laser treatments can provide long-lasting results, especially for conditions like sunspots and freckles. However, factors such as continued sun exposure and hormonal changes can cause new pigmentation to develop over time. To maintain the results, it’s important to follow a good skincare routine, including the use of sunscreen and other preventive measures.
Risks and Side Effects of Laser Pigmentation Treatment
Common Side Effects
While laser treatments for pigmentation are generally safe, they do come with some potential side effects, especially when not performed by a skilled and experienced practitioner. Common side effects include:
Redness and swelling: Temporary redness and swelling are common after laser treatment. These side effects usually resolve within a few days.
Crusting and peeling: In some cases, the treated areas may develop a crust or peel as the pigmented skin cells are shed.
Hyperpigmentation or hypopigmentation: Some individuals may experience post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation (PIH) or hypopigmentation (lightening of the skin) as a result of the laser treatment. This is more common in individuals with darker skin tones, though newer laser technologies, like the Pico laser, have minimized this risk.
How to Minimize Risks
To minimize the risk of side effects, it’s crucial to choose a qualified and experienced dermatologist or laser technician. They can assess your skin type and pigmentation issues to recommend the most appropriate laser treatment. Additionally, following post-treatment care instructions, such as avoiding sun exposure and using sunscreen, is essential to reduce the risk of complications.
Alternative Treatments for Pigmentation
While lasers are highly effective for treating pigmentation, they may not be suitable for everyone. Some people may prefer non-laser alternatives or may need to combine laser treatment with other methods for better results. These alternatives include:
1. Topical Treatments
There are various topical treatments that can help lighten pigmentation over time, including:
Hydroquinone: A skin-lightening agent that reduces melanin production.
Retinoids: Vitamin A derivatives that increase skin cell turnover and can fade dark spots.
Vitamin C: An antioxidant that helps brighten the skin and reduce pigmentation.
Azelaic Acid: Another topical agent that can inhibit melanin production.
2. Chemical Peels
Chemical peels use acids, such as glycolic acid or salicylic acid, to exfoliate the skin and reduce pigmentation. They are often used to treat superficial pigmentation issues and can be combined with laser treatments for more stubborn pigmentation.
3. Microdermabrasion
Microdermabrasion is a non-invasive procedure that exfoliates the outermost layer of the skin. It can be effective for mild pigmentation issues, but may not be sufficient for deeper pigmentation concerns.
4. Cryotherapy
Cryotherapy involves freezing the pigmented areas with liquid nitrogen, causing the pigmented skin to peel away. This treatment is typically used for small, isolated spots, such as sunspots or age spots.
Conclusion
The answer is yes—laser treatments can effectively remove or significantly reduce skin pigmentation in many cases. With advances in laser technology, treatments are now more precise, safe, and effective than ever before. The choice of laser treatment depends on the type and severity of the pigmentation, as well as the patient’s skin type.
However, it’s important to approach laser treatment with realistic expectations. While many patients experience dramatic improvements, results can vary based on individual skin conditions and response to treatment. Moreover, maintenance treatments and good skincare habits, particularly sun protection, are essential to prevent new pigmentation from developing.
Laser treatments are a powerful tool in the fight against unwanted pigmentation, but as with any medical procedure, consultation with a qualified professional is key to achieving the best results.
Related topic:
What Is The Best Laser Treatment for Smokers’ Lines?
Can CO2 Laser Remove Freckles?
Is Laser More Painful Than Waxing?