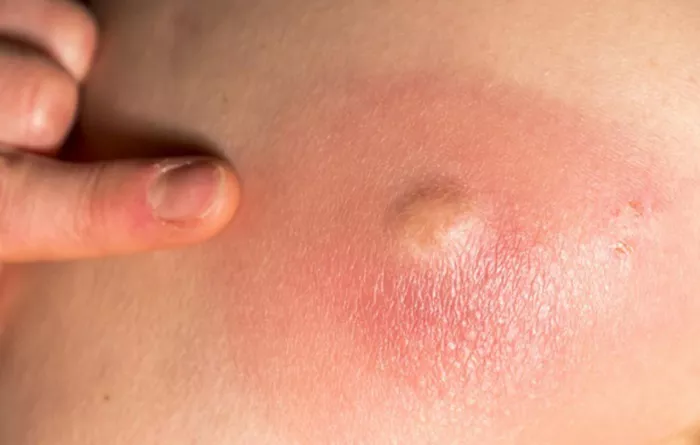
Boils are painful, pus-filled lumps that can develop on the skin due to bacterial infections, often caused by Staphylococcus aureus. They can appear anywhere on the body but are most commonly found in areas where hair follicles are present, such as the face, neck, armpits, and thighs. While boils can be uncomfortable and unsightly, many small boils can be effectively treated at home without the need for medical intervention. This article will provide a comprehensive guide on how to care for a boil at home, including symptoms, causes, and effective home remedies.
Understanding Boils
What is a Boil?
A boil, also known as a furuncle, is a localized infection that results in a lump filled with pus. The skin around the boil may appear red and swollen, and it can be tender to the touch. Boils typically develop when bacteria infect hair follicles or oil glands.
Symptoms of Boils
Common symptoms associated with boils include:
Redness: The skin around the boil becomes red and inflamed.
Swelling: The area may swell as the infection progresses.
Pain: Boils can be painful, especially when touched.
Pus-filled lump: A noticeable lump filled with yellow or white pus forms at the center.
Fever: In some cases, a person may experience fever or chills if the infection spreads.
Causes of Boils
Boils are primarily caused by bacterial infections. Factors that may increase the likelihood of developing boils include:
Poor hygiene: Inadequate cleaning of the skin can lead to infections.
Skin conditions: Conditions like acne or eczema can contribute to boil formation.
Weakened immune system: Individuals with compromised immune systems are more susceptible.
Obesity: Excess weight can create skin folds where bacteria thrive.
Close contact with infected individuals: Sharing personal items or close physical contact can spread bacteria.
Home Care for Boils
Taking care of a boil at home involves several steps aimed at alleviating pain, promoting healing, and preventing further infection. Below are detailed methods for managing boils effectively.
Warm Compresses
Applying Warm Compresses
One of the most effective home remedies for treating boils is using warm compresses. Heat helps increase blood circulation to the affected area, bringing more white blood cells to fight infection.
- Soak a clean washcloth in warm water.
- Wring out excess water so that it is damp but not dripping.
- Apply the warm compress to the boil for 10 to 15 minutes.
- Repeat this process 3 to 4 times daily until the boil drains naturally.
This method not only helps reduce pain but also encourages the boil to come to a head and drain naturally.
Keeping It Clean
Hygiene Practices
Maintaining cleanliness around the boil is crucial to prevent further infection:
- Wash your hands thoroughly before and after touching the boil.
- Use an antibacterial soap to gently cleanse the area around the boil twice daily.
- Pat dry with a clean towel; do not rub as this may irritate the area further.
Pain Relief
Over-the-Counter Pain Relief
To manage pain associated with boils:
Consider taking over-the-counter medications such as ibuprofen (Advil) or acetaminophen (Tylenol) as directed on the packaging.
Do Not Squeeze or Pop
Avoid Manipulating the Boil
It is essential not to squeeze or attempt to pop a boil. Doing so can push bacteria deeper into the skin and lead to more severe infections or complications.
Covering the Boil
Using Dressings
Once a boil starts draining:
- Cover it with a sterile bandage or gauze to protect it from dirt and bacteria.
- Change the dressing regularly and keep it clean until it heals completely.
Natural Remedies
Several natural remedies may help alleviate symptoms and promote healing:
Tea Tree Oil
Tea tree oil has strong antibacterial properties that may help treat boils:
- Mix five drops of tea tree oil with one teaspoon of carrier oil (like coconut or olive oil).
- Apply this mixture gently around (but not directly on) the boil using a cotton ball.
This method should be used cautiously, as tea tree oil can irritate sensitive skin.
Turmeric Paste
Turmeric contains curcumin, which has anti-inflammatory properties:
- Mix turmeric powder with water to create a paste.
- Apply this paste directly onto the boil and cover it with a bandage.
- Leave it on for several hours before rinsing off.
This remedy may help reduce swelling and promote healing.
Epsom Salt Soak
Epsom salt can help draw out impurities from boils:
- Dissolve Epsom salt in warm water in a bathtub or basin.
- Soak in this solution for 15–20 minutes daily.
This method can relieve discomfort and assist in drainage.
When to Seek Medical Attention
While many boils can be treated at home, certain situations warrant professional medical evaluation:
- If you have had a boil for more than two weeks without improvement.
- If you experience recurrent boils (more than one at a time).
- If you notice fever or chills accompanying your symptoms.
- If the boil is located on your face or spine.
- If there is excessive redness or swelling around the boil, indicating potential spreading infection.
Medical Treatments
In some cases, medical intervention may be necessary:
Incision and Drainage
If a boil does not drain naturally, your healthcare provider may perform an incision and drainage procedure:
- The doctor will numb the area with local anesthesia.
- A small incision will be made in the boil to allow pus to escape.
- The area will then be packed with sterile gauze if necessary.
This procedure helps relieve pain and promotes faster healing.
Antibiotics
For severe or recurrent boils, antibiotics may be prescribed:
- Your doctor will determine if antibiotics are necessary based on your symptoms and overall health condition.
- Follow your doctor’s instructions regarding dosage and duration of treatment.
Antibiotics help eliminate bacteria causing infections and prevent complications.
Preventing Future Boils
To reduce your risk of developing future boils, consider implementing these preventive measures:
1. Maintain Good Hygiene
Regularly wash your hands and keep your skin clean:
- Bathe daily using antibacterial soap.
- Wash towels and bedding frequently in hot water.
2. Avoid Sharing Personal Items
Do not share personal items such as towels, razors, or clothing with others who have boils or other skin infections35.
3. Manage Underlying Health Conditions
If you have conditions like diabetes or obesity that increase your risk for boils:
- Work closely with your healthcare provider to manage these conditions effectively.
- Follow recommended dietary guidelines and exercise routines.
4. Keep Skin Moisturized
Dry skin can lead to cracks where bacteria enter:
Use moisturizers regularly on dry areas of your skin.
5. Wear Loose Clothing
Avoid tight clothing that creates friction against your skin:
Choose breathable fabrics that allow air circulation.
Conclusion
Boils are common skin infections that typically resolve on their own but can cause significant discomfort. Home care strategies such as applying warm compresses, maintaining cleanliness, and using natural remedies can effectively treat small boils without medical intervention. However, it’s essential to monitor symptoms closely and seek medical attention if complications arise or if symptoms persist beyond two weeks. By understanding how to care for boils at home and implementing preventive measures, you can manage this condition effectively while minimizing future occurrences.
Related topic:
What Is The Best Face Wash For Milia?
What Is The Best Multi Action Sculpting Cream?