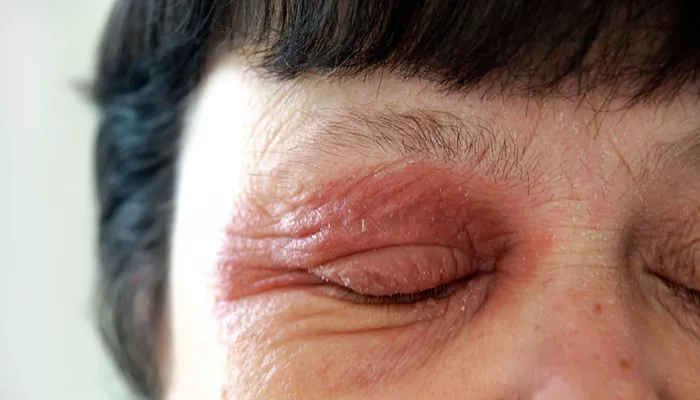
Dermatitis around the eyes, often referred to as eyelid dermatitis or periocular dermatitis, is a common skin condition that can cause significant discomfort and distress. This type of dermatitis can manifest as redness, itching, swelling, and flaking of the skin around the eyes. The delicate nature of the skin in this area makes it particularly susceptible to various irritants and allergens. Understanding how to effectively manage and treat dermatitis around the eyes is crucial for maintaining not only skin health but also overall well-being.
This article provides an in-depth overview of dermatitis around the eyes, including its causes, symptoms, and effective treatment options. We will explore both medical and home remedies that can help alleviate symptoms and prevent flare-ups. By following these guidelines, individuals suffering from this condition can find relief and improve their quality of life.
Understanding Dermatitis Around the Eyes
What Is Dermatitis?
Dermatitis is a general term that describes inflammation of the skin. It can occur anywhere on the body, but when it affects the area around the eyes, it is specifically termed eyelid dermatitis. This condition can result from various factors, including allergies, irritants, or underlying skin conditions.
Types of Dermatitis
There are several types of dermatitis that can affect the eye area:
Atopic Dermatitis: Often associated with allergies and asthma, atopic dermatitis is a chronic condition that can cause dry, itchy skin.
Contact Dermatitis: This occurs when the skin reacts to a specific substance or allergen, such as cosmetics or skincare products.
Seborrheic Dermatitis: This type is characterized by red, flaky patches and is often associated with oily skin.
Nummular Dermatitis: This presents as coin-shaped patches on the skin and can be triggered by dry skin or irritation.
Symptoms of Dermatitis Around the Eyes
Common symptoms of eyelid dermatitis include:
- Redness and inflammation
- Itching or burning sensation
- Dryness or flaking skin
- Swelling of the eyelids
- Crusty patches or weeping sores in severe cases
Recognizing these symptoms early can help in seeking appropriate treatment.
Causes of Dermatitis Around the Eyes
Allergens and Irritants
The skin around the eyes is particularly sensitive. Common triggers include:
Cosmetics: Eye makeup such as mascara, eyeliner, and eyeshadow can irritate sensitive skin.
Skincare Products: Certain creams or lotions may contain fragrances or preservatives that provoke a reaction.
Environmental Factors: Pollutants, dust, and pollen can exacerbate symptoms.
Contact Lenses: Improper use or allergic reactions to lens materials can lead to irritation.
Underlying Conditions
Certain health conditions may predispose individuals to develop dermatitis around the eyes:
Eczema: Individuals with a history of eczema are more likely to experience eyelid dermatitis.
Psoriasis: This chronic autoimmune condition may also affect the eyelids.
Rosacea: This inflammatory skin condition can lead to redness and irritation around the eyes.
Diagnosis of Dermatitis Around the Eyes
A healthcare professional typically diagnoses eyelid dermatitis through a physical examination and patient history. In some cases, allergy testing may be recommended to identify specific triggers. If symptoms persist despite treatment, further evaluation may be necessary to rule out other conditions.
Treatment Options for Dermatitis Around the Eyes
Home Remedies
For mild cases of dermatitis around the eyes, several home remedies may provide relief:
Cold Compresses: Applying a cold compress can help reduce swelling and soothe itching.
Moisturizers: Using a thick, unscented moisturizer can help keep the skin hydrated. Products like petroleum jelly (Vaseline) are effective for creating a protective barrier.
Gentle Cleansers: Washing with mild cleansers free from fragrances helps avoid further irritation.
Medical Treatments
In more severe cases or when home remedies are ineffective, medical treatments may be necessary:
1. Topical Corticosteroids
Topical corticosteroids are commonly prescribed to reduce inflammation and itching. Mild steroids like hydrocortisone (0.5%-1%) are often recommended for short-term use on affected areas. More potent steroids may be prescribed for severe flare-ups but should be used cautiously due to potential side effects like thinning of the skin.
2. Topical Calcineurin Inhibitors
Topical calcineurin inhibitors (TCIs), such as tacrolimus (Protopic) and pimecrolimus (Elidel), are non-steroidal medications that help manage inflammation without thinning the skin. They are particularly useful for long-term management in sensitive areas like around the eyes137.
3. Antihistamines
Oral antihistamines may be recommended if itching is severe or if allergies are suspected as a trigger. These medications help reduce allergic reactions and provide symptomatic relief.
4. Antibiotics
If there is a secondary bacterial infection due to scratching or broken skin, topical or oral antibiotics may be prescribed.
5. Phototherapy
In some cases where conventional treatments fail, phototherapy (light therapy) may be considered as an option for managing chronic dermatitis.
Preventive Measures for Dermatitis Around the Eyes
Identify Triggers
Keeping a diary to track flare-ups can help identify specific triggers. Once identified, avoiding these irritants is crucial in preventing future outbreaks.
Maintain Good Hygiene
Practicing good hygiene is essential:
- Wash hands frequently before touching your face.
- Use clean towels and avoid sharing personal items like makeup brushes.
Use Gentle Products
Choosing skincare products labeled “hypoallergenic” and “fragrance-free” minimizes exposure to potential irritants. Always patch-test new products before applying them near the eyes.
Moisturize Regularly
Regularly applying moisturizers helps maintain skin hydration and integrity. Opt for thicker formulations that create a barrier against environmental factors.
Limit Makeup Use During Flare-Ups
Avoid using makeup during active flare-ups to prevent further irritation. When makeup is used, ensure it is hypoallergenic and designed for sensitive skin.
Lifestyle Adjustments
Making certain lifestyle changes can also contribute positively to managing dermatitis:
1. Diet Considerations
Some individuals find that certain foods may trigger their eczema symptoms. Keeping a food diary may help identify any dietary triggers that could exacerbate dermatitis.
2. Stress Management
Stress is known to worsen eczema symptoms; therefore, incorporating stress-reducing activities such as yoga, meditation, or regular exercise into your routine can be beneficial.
3. Environmental Control
Using humidifiers in dry environments helps maintain moisture levels in the air, which can prevent dry skin flare-ups. Additionally, protecting your face from extreme weather conditions—like cold winds—can also help manage symptoms.
Conclusion
Dermatitis around the eyes can significantly impact daily life due to its uncomfortable symptoms and visible nature. Understanding its causes and implementing effective treatment strategies—both medical and home-based—can lead to successful management of this condition. By identifying triggers, maintaining proper skincare routines, and seeking appropriate medical advice when necessary, individuals suffering from eyelid dermatitis can find relief and improve their quality of life.
With proper care and attention to skincare practices, it is possible to minimize flare-ups and maintain healthy skin around the eyes. Always consult with a healthcare professional for personalized advice tailored to individual needs and circumstances regarding treatment options for dermatitis around the eyes.
Related topic:
How to Treat Dry Skin Around the Eyes?
How to Reduce Swelling on the Upper Eyelid?