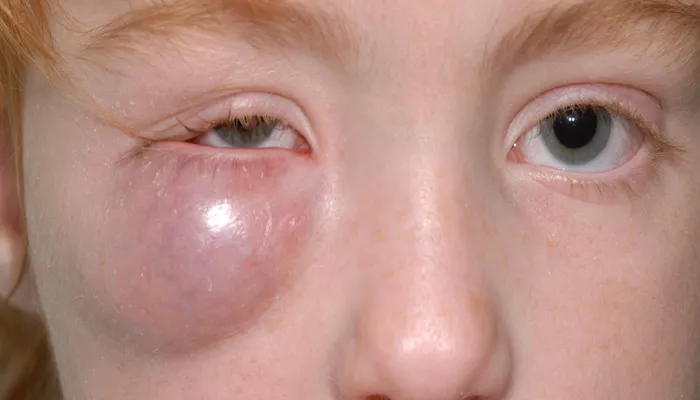
Periorbital edema, commonly referred to as puffy eyes, is a condition characterized by swelling around the eyes. This swelling can occur in one or both eyes and is caused by fluid accumulation in the tissues surrounding the eye, known as the eye orbit. The appearance of periorbital edema can range from mild puffiness to significant swelling that may partially close the eyelids. While often temporary and not serious, periorbital edema can sometimes indicate underlying health issues that require attention.
Causes of Periorbital Edema
The causes of periorbital edema are diverse, encompassing lifestyle factors, medical conditions, and environmental influences. Understanding these causes is crucial for effective treatment.
Lifestyle Factors
Dietary Choices: A high-salt diet can lead to fluid retention, contributing to swelling around the eyes. Reducing salt intake may help alleviate this condition.
Sleep Patterns: Irregular sleep patterns, whether too little or too much sleep, can cause fluid retention and lead to periorbital edema.
Alcohol Consumption: Excessive alcohol intake can dehydrate the body, prompting it to retain fluids and resulting in puffiness around the eyes.
Smoking: Smoking affects hormonal balance and blood circulation, which may contribute to fluid retention.
Crying: Prolonged crying can irritate the eyes and cause temporary swelling due to inflammation.
Medical Conditions
Allergies: Allergic reactions can cause inflammation in the small blood vessels around the eyes, leading to swelling. Common allergens include pollen, dust mites, and pet dander.
Thyroid Disorders: Conditions like hypothyroidism or hyperthyroidism can lead to fluid retention around the eyes.
Kidney Issues: Kidney diseases can disrupt fluid balance in the body, resulting in periorbital edema.
Infections: Infections such as sinusitis or periorbital cellulitis can cause inflammation and swelling around the eyes.
Aging: As people age, skin elasticity decreases, which may contribute to a more pronounced appearance of puffiness.
Symptoms of Periorbital Edema
Symptoms associated with periorbital edema vary based on the underlying cause but generally include:
- Swelling around one or both eyes
- Redness or inflammation
- Sensitivity to light
- Itching or burning sensations
- Discomfort or pain when moving the eye
- Excessive tearing
In some cases, individuals may experience additional symptoms related to underlying conditions, such as fever in infections or systemic symptoms in autoimmune disorders.
Diagnosis of Periorbital Edema
Diagnosing periorbital edema involves a thorough medical history and physical examination. Healthcare providers will assess symptoms and may conduct tests to identify underlying causes.
Medical History Review
The physician will inquire about:
- Recent illnesses or infections
- Allergies
- Dietary habits
- Sleep patterns
- Medication use
Physical Examination
A physical examination will focus on:
- The extent of swelling
- Redness or other signs of inflammation
- Any associated symptoms like pain or vision changes
Diagnostic Tests
If necessary, additional tests may be conducted:
- Blood Tests: To check for kidney function, thyroid levels, and signs of infection.
- Imaging Studies: CT scans or MRIs may be used to evaluate for structural abnormalities or infections.
- Allergy Testing: If allergies are suspected as a cause.
Treatment Options for Periorbital Edema
The treatment for periorbital edema largely depends on its underlying cause. Here are several approaches that may be recommended:
1. Lifestyle Modifications
Dietary Changes:
Reduce salt intake to minimize fluid retention.
Increase hydration by drinking plenty of water.
Sleep Hygiene:
Aim for 7-9 hours of quality sleep each night.
Elevate your head while sleeping to prevent fluid accumulation.
Limit Alcohol and Quit Smoking:
Reducing alcohol consumption can help maintain hydration levels.
Quitting smoking improves overall health and circulation.
2. Home Remedies
Cold Compresses:
Applying cold compresses or chilled tea bags can reduce swelling and soothe inflammation.
Hydration:
Staying well-hydrated helps flush out excess sodium from the body.
Cucumber Slices:
Placing cucumber slices on closed eyelids may provide a cooling effect and reduce puffiness.
3. Medical Treatments
Antihistamines:
For allergic reactions causing periorbital edema, antihistamines can alleviate symptoms.
Topical Treatments:
Creams containing caffeine or other active ingredients may help reduce puffiness temporarily.
Prescription Medications:
In cases related to thyroid disorders or kidney issues, specific medications may be necessary to manage these conditions effectively.
4. Surgery:
In severe cases where structural issues cause persistent swelling (e.g., tumors), surgical intervention might be required.
Preventing Periorbital Edema
While not all cases of periorbital edema are preventable, certain strategies can help minimize its occurrence:
- Maintain a balanced diet low in salt.
- Practice good sleep hygiene.
- Manage allergies effectively with appropriate medications.
- Stay hydrated and limit alcohol consumption.
- Regularly consult with healthcare providers for chronic conditions affecting fluid balance.
Conclusion
Periorbital edema is a common condition that can arise from various lifestyle factors and medical issues. Understanding its causes and symptoms is essential for effective management and treatment. By implementing lifestyle changes and seeking appropriate medical care when necessary, individuals can reduce their risk of developing periorbital edema and maintain healthier skin around their eyes.
In summary, addressing lifestyle factors such as diet, sleep patterns, and hydration plays a crucial role in preventing this condition while also ensuring that any underlying medical issues are promptly treated will help alleviate symptoms effectively.
Related topic:
How To Reduce Eye Swelling From Allergies?
What Is The Best Treatment For Fluid Under Eyes?
What Is The Medicine For Swollen Eyes?