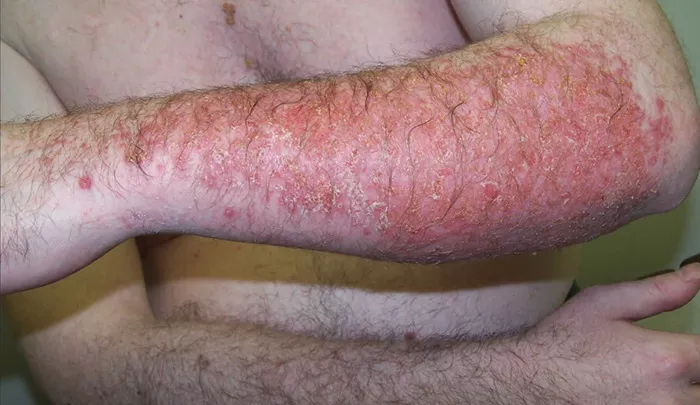
Dermatitis is a common skin condition that affects millions of people worldwide. It can be uncomfortable, itchy, and sometimes even painful. The good news is that with the right approach, you can manage and clear up dermatitis effectively. In this article, we will explore what dermatitis is, its different types, and the best ways to treat and prevent it.
What Is Dermatitis?
Dermatitis is a general term that describes inflammation of the skin. It can manifest in various forms, each with its own set of symptoms and triggers. The most common symptoms include redness, itching, swelling, and sometimes blistering. Dermatitis is not contagious, but it can be chronic, meaning it can last for a long time or recur frequently.
Types of Dermatitis
There are several types of dermatitis, each with unique characteristics:
- Atopic Dermatitis (Eczema): This is a chronic condition that often starts in childhood. It is characterized by dry, itchy skin and can be triggered by allergens, stress, or environmental factors.
- Contact Dermatitis: This occurs when the skin comes into contact with an irritant or allergen. It can be either irritant contact dermatitis (caused by substances like chemicals) or allergic contact dermatitis (triggered by allergens like poison ivy).
- Seborrheic Dermatitis: This type affects areas of the skin with a high number of oil glands, such as the scalp, face, and chest. It is often associated with dandruff and can be influenced by hormonal changes or yeast overgrowth.
- Nummular Dermatitis: This form is characterized by coin-shaped patches of irritated skin. It is often triggered by dry skin, environmental factors, or stress.
- Stasis Dermatitis: This occurs in people with poor circulation, often in the lower legs. It is associated with swelling, varicose veins, and skin changes.
Causes and Triggers of Dermatitis
Understanding the causes and triggers of dermatitis is crucial for effective management. While the exact cause can vary depending on the type of dermatitis, some common factors include:
- Genetics: A family history of eczema, asthma, or allergies can increase the risk of developing atopic dermatitis.
- Environmental Factors: Exposure to irritants like chemicals, detergents, or pollutants can trigger contact dermatitis.
- Allergens: Substances like pollen, pet dander, or certain foods can exacerbate symptoms in sensitive individuals.
- Stress: Emotional stress can worsen dermatitis symptoms, particularly in atopic dermatitis.
- Weather: Cold, dry weather can lead to dry skin, which can trigger or worsen dermatitis.
- Infections: Bacterial or fungal infections can sometimes lead to dermatitis, especially in seborrheic dermatitis.
How To Clear Up Dermatitis: Treatment Options
Clearing up dermatitis involves a combination of lifestyle changes, skincare routines, and medical treatments. Here are some effective strategies:
1. Moisturize Regularly
Keeping your skin well-hydrated is one of the most important steps in managing dermatitis. Use a thick, fragrance-free moisturizer to lock in moisture and prevent dryness. Apply it immediately after bathing to seal in hydration.
2. Avoid Triggers
Identify and avoid substances or situations that trigger your dermatitis. This could include certain soaps, detergents, fabrics, or foods. Keeping a diary of your symptoms can help you pinpoint potential triggers.
3. Use Topical Corticosteroids
Topical corticosteroids are commonly prescribed to reduce inflammation and itching. They come in various strengths, so it’s important to use them as directed by your healthcare provider. Overuse can lead to skin thinning, so follow the recommended guidelines.
4. Try Calcineurin Inhibitors
For those who cannot use corticosteroids, calcineurin inhibitors like tacrolimus or pimecrolimus can be effective. These medications help reduce inflammation and are particularly useful for sensitive areas like the face.
5. Take Antihistamines
Oral antihistamines can help relieve itching, especially at night. Non-drowsy options are available for daytime use, while sedating antihistamines can help you sleep better if nighttime itching is a problem.
6. Consider Phototherapy
For severe cases of dermatitis, phototherapy (light therapy) may be recommended. This involves exposing the skin to controlled amounts of natural or artificial ultraviolet light to reduce inflammation and improve symptoms.
7. Use Wet Wrap Therapy
Wet wrap therapy involves applying a damp layer of bandages or clothing over moisturized skin. This can help lock in moisture and reduce itching and inflammation. It is particularly useful for children with severe eczema.
8. Manage Stress
Since stress can exacerbate dermatitis, finding ways to manage stress is crucial. Techniques like yoga, meditation, and deep breathing exercises can help reduce stress levels and improve overall skin health.
9. Maintain a Healthy Diet
A balanced diet rich in anti-inflammatory foods can support skin health. Foods high in omega-3 fatty acids, such as salmon and flaxseeds, can help reduce inflammation. Avoid foods that trigger your symptoms, if any.
10. Consult a Dermatologist
If over-the-counter treatments and lifestyle changes are not effective, it’s important to consult a dermatologist. They can provide a personalized treatment plan, which may include prescription medications or advanced therapies.
Preventing Dermatitis Flare-Ups
Prevention is key to managing dermatitis in the long term. Here are some tips to help prevent flare-ups:
- Choose Gentle Skincare Products: Opt for fragrance-free, hypoallergenic products that are designed for sensitive skin.
- Wear Soft, Breathable Fabrics: Avoid rough or synthetic fabrics that can irritate the skin. Cotton is usually a safe choice.
- Keep Your Nails Short: Short nails can help prevent scratching, which can worsen dermatitis and lead to infections.
- Avoid Hot Showers: Hot water can strip the skin of its natural oils, leading to dryness. Use lukewarm water instead.
- Humidify Your Home: Using a humidifier can help maintain moisture levels in the air, especially during dry winter months.
- Stay Hydrated: Drinking plenty of water helps keep your skin hydrated from the inside out.
When To Seek Medical Attention
While most cases of dermatitis can be managed at home, there are times when medical attention is necessary. Seek help if:
- Your symptoms are severe or worsening despite treatment.
- You experience signs of infection, such as pus, redness, or fever.
- Your dermatitis is affecting your quality of life or mental health.
- You have open sores or cracks in the skin that are not healing.
Conclusion
Dermatitis can be a challenging condition to live with, but with the right approach, it is possible to clear up the symptoms and prevent flare-ups. By understanding your triggers, following a consistent skincare routine, and seeking professional help when needed, you can manage dermatitis effectively. Remember, everyone’s skin is different, so what works for one person may not work for another. Be patient and persistent in finding the best treatment plan for you.
Taking care of your skin is not just about treating symptoms; it’s about adopting a holistic approach that includes lifestyle changes, stress management, and proper skincare. With time and effort, you can achieve clearer, healthier skin and improve your overall well-being.
Related topic:
What To Put On Skin After Popping Pimples?
Can Antibacterial Soap Cause Eczema?
How To Get Rid Of Heat Rash Bumps?